Introduction: Why Heart Health Matters in Summer
Heart Attack Symptoms in Adults often become more noticeable during extreme heat, making it crucial to protect your heart during the dog days of summer. As record-breaking heat waves become more frequent, cardiovascular health is placed under greater strain. During the summer months, particularly in 2023, many regions of the United States experienced extreme temperatures that led to a surge in emergency visits for heat-related illnesses. Individuals with existing heart conditions, high blood pressure, or metabolic disorders face elevated risks when exposed to high heat combined with environmental stressors like air pollution. Understanding how heat impacts the heart and learning to recognize early warning signs can be life-saving.
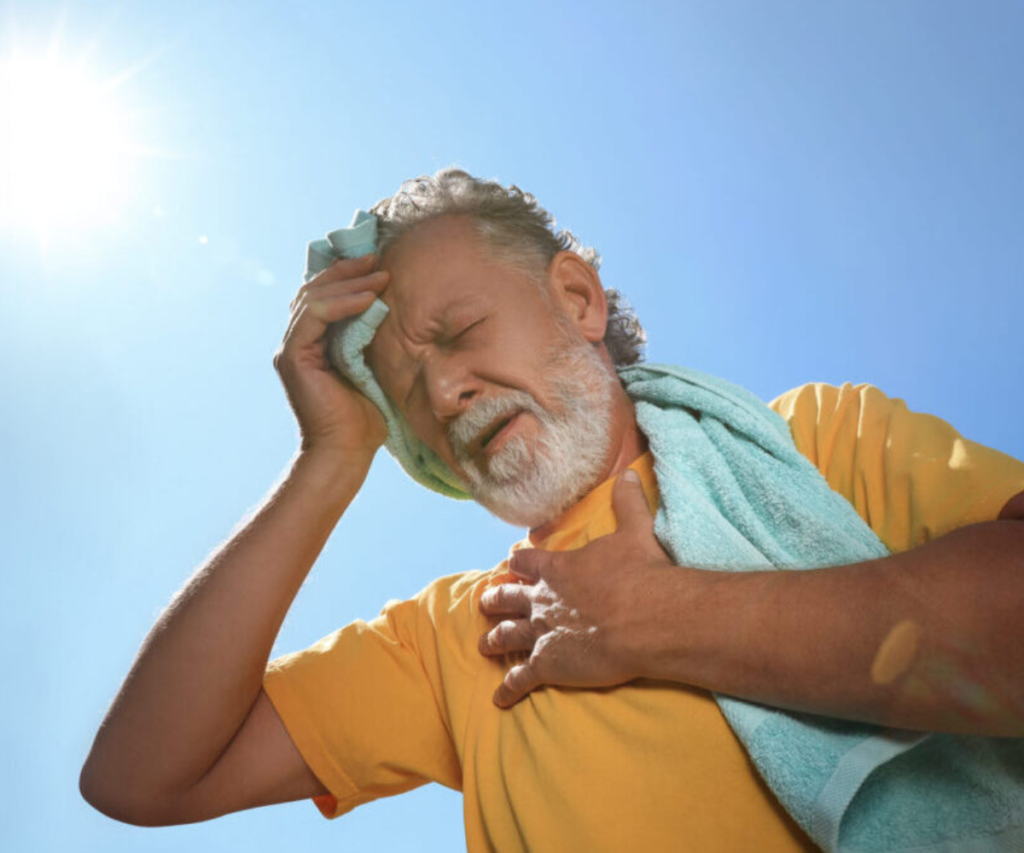

Climate change has extended the duration and severity of hot days, intensifying the pressure on the cardiovascular system. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can worsen underlying conditions and increase the likelihood of cardiac events. Recognizing heart attack symptoms in adults early, planning outdoor activities wisely, and following preventive strategies are essential steps to maintain a healthy heart throughout summer.
How High Temperatures Affect the Heart
High temperatures impose extra stress on the cardiovascular system. The heart works harder to pump blood, both to the muscles and to the skin, helping the body release heat. When air temperature nears or exceeds body temperature—roughly 98°F—the body’s natural cooling mechanisms, such as sweating and heat radiation, become less effective.
Humidity further complicates the body’s cooling process. Sweat evaporates into the air to remove heat from the skin. When relative humidity climbs above 75%, evaporation slows down, leaving the body more prone to overheating. Heat stress forces the heart to pump additional blood, which increases cardiac workload and can lead to irregular heart rhythms, palpitations, or even heart attacks in vulnerable individuals.
Recognizing the Warning Signs of Heat Stress
Knowing the signs of heat stress can prevent severe cardiac complications. Common indicators include:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Excessive sweating or, conversely, lack of sweat in extreme cases
- Headaches or confusion
- Shortness of breath
Severe cases may progress to heat exhaustion or heatstroke, both of which require immediate medical attention. Heatstroke can result in organ failure, unconsciousness, or cardiac arrest if not treated promptly.
Hot-Weather Exercise Guidelines
Exercise remains important during the summer, but modifications are necessary to reduce cardiovascular strain. Safe strategies include:
1. Timing Your Workouts
Avoid outdoor exercise during the hottest part of the day, typically between noon and 3 p.m. Early morning or late evening sessions minimize exposure to peak temperatures.
2. Dressing Appropriately
Lightweight, loose-fitting, light-colored clothing made from sweat-wicking materials allows better airflow and accelerates sweat evaporation. Breathable fabrics help maintain core temperature and reduce cardiac stress.
3. Staying Hydrated
Water intake is essential. Drink water before, during, and after activity. For prolonged sessions lasting more than an hour, sports drinks containing electrolytes—such as potassium, sodium, and magnesium—help replenish minerals lost through sweat. Individuals taking diuretics or blood pressure medications should monitor hydration levels carefully, as they are more prone to dehydration.
4. Cooling Alternatives
On extremely hot days, consider exercising in water (swimming or water aerobics) or indoors in an air-conditioned environment. These alternatives reduce cardiac load and maintain safe core temperatures.
Understanding Air Quality and Its Effects on the Heart
Summer heat accelerates chemical reactions in the atmosphere, producing smog and increasing particulate pollution. Sources include vehicle emissions, industrial output, wildfires, and dust. Tiny airborne particles, known as PM2.5, are smaller than 2.5 microns in diameter. These particles bypass the upper airway and reach the bloodstream, triggering inflammation, oxidative stress, and increased heart rate variability. Heart Attack Symptoms in Adults.
Even low levels of air pollution can increase the risk of:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Irregular heart rhythms
Monitoring local air quality is essential, particularly during exercise. Smartphone weather apps and government resources, such as the Environmental Protection Agency’s AirNow, provide real-time air quality updates.
Nutrition for Summer Heart Health
Diet can support cardiovascular function and help regulate body temperature. Key strategies include:
- Hydrating foods: Fruits like watermelon, cucumber, and oranges provide water and electrolytes.
- Magnesium-rich foods: Nuts, seeds, and leafy greens support heart rhythm stability.
- Lean protein: Helps maintain muscle mass without contributing to excessive metabolic heat.
- Light, balanced meals: Avoid heavy, fried, or highly processed foods that increase metabolic load and heat generation.
Medication Considerations
Certain medications can affect hydration, blood pressure, and heart rate, particularly in hot weather. These include:
- Diuretics: Increase urine output and can exacerbate dehydration.
- Beta-blockers: May limit heart rate response to heat stress.
- ACE inhibitors/ARBs: May affect electrolyte balance during prolonged sweating.
Consulting a healthcare provider before high-heat activities ensures medication regimens are adjusted safely.
Home and Environmental Cooling Strategies
Not all households have air conditioning. Simple strategies can help:
- Use fans and cross-ventilation to circulate air.
- Keep blinds or curtains closed during peak sunlight hours.
- Take cool showers or use damp cloths to lower skin temperature.
- Hydrate with cold beverages and ice-infused water.

For those with heart conditions, maintaining a cool home environment is critical to reducing cardiac strain. Protect your heart during the dog days of summer. Heart Attack Symptoms in Adults.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-eVJhlIyFLg
Traveling and Vacation Safety
Summer vacations often involve heat exposure and air travel. Tips include:
- Stay hydrated during flights and avoid alcohol and caffeine.
- Schedule outdoor sightseeing during morning or evening hours.
- Check local air quality forecasts before visiting cities prone to pollution.
- Seek accommodations with climate control.
Lifestyle and Long-Term Strategies
Protecting the heart during the summer is not just about immediate precautions. Long-term strategies include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce cardiac workload.
- Building cardiovascular endurance gradually to withstand heat stress.
- Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques to lower stress-induced cardiac strain.
- Regularly monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Protect your heart during the dog days of summer.
Actionable Checklist for Summer Heart Safety
- Hydrate regularly, with water and electrolyte drinks
- Avoid outdoor activity during peak heat
- Wear light, breathable clothing
- Exercise indoors or in water when temperatures exceed safe limits
- Monitor air quality before outdoor activities
- Include heart-healthy foods in your diet
- Adjust medications with healthcare provider guidance
- Cool your living environment proactively
- Recognize and respond promptly to heat stress symptoms
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How long can the heart safely cope with extreme heat?
A: Duration depends on fitness, hydration, and underlying health. Limit strenuous outdoor activity during peak heat and take frequent breaks. Heart Attack Symptoms in Adults.
Q: Can air conditioning alone prevent heat-related heart problems?
A: Air conditioning reduces risk, but hydration, exercise timing, and diet remain important factors.
Q: Are all heart patients equally vulnerable to heat stress?
A: Individuals with heart failure, arrhythmias, or high blood pressure are particularly at risk.
Q: What is the safest indoor exercise in summer?
A: Swimming, stationary cycling, and air-conditioned treadmill workouts minimize cardiac strain.
Conclusion

The dog days of summer present unique challenges to heart health. Extreme heat, high humidity, and air pollution increase cardiovascular risk, particularly for individuals with preexisting conditions. Adopting preventive strategies—hydration, exercise timing, clothing choices, indoor alternatives, diet, and air quality monitoring—can help safeguard your heart. By understanding the science behind heat stress and air pollution, making informed lifestyle choices, and responding promptly to warning signs, it is possible to enjoy summer safely while maintaining optimal cardiovascular health. Protect your heart during the dog days of summer. Heart Attack Symptoms in Adults.