Protecting Your Digital Wallet: The Rise of Mobile Payment Security

As mobile payment systems become increasingly integrated into everyday life, the security of these digital wallets has never been more critical. Consumers are rapidly adopting technologies like Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and various banking apps, which promise convenience but also pose new challenges and risks. This article delves into the evolution of mobile payment security, the mechanisms that protect users, and the best practices to safeguard your digital wallet.
The Evolution of Mobile Payment Security
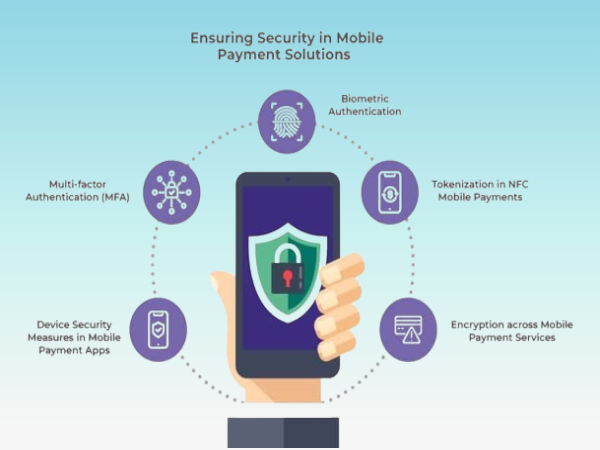
Encryption: One of the foundational elements of mobile payment security is encryption. Data transmitted during transactions is encrypted, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept and decipher it. Modern encryption standards, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), ensure that sensitive information remains protected.
- Advertisement -Tokenization: Tokenization is another critical security measure. Instead of transmitting actual credit card numbers, the system generates a unique token for each transaction. This token is useless to hackers if intercepted, as it cannot be traced back to the original card information.
Biometric Authentication: The introduction of biometric authentication, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, has added an extra layer of security. These methods ensure that only the authorized user can initiate a transaction, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Many mobile payment systems now require two-factor authentication. In addition to entering a password, users must verify their identity through a second method, such as a text message code or a biometric scan. This makes it significantly harder for hackers to gain access to accounts.
Current Security Mechanisms

Secure Element Technology: Some devices use a secure element (SE), a dedicated chip that securely stores payment information. This chip is isolated from the device’s main operating system, making it harder for malware to access sensitive data.
Host Card Emulation (HCE): HCE allows mobile devices to emulate a smart card, enabling contactless payments without needing a secure element. While HCE relies more on software security measures, it is designed to work with cloud-based tokenization to ensure transactions are safe.
Regular Security Updates: Developers continuously update mobile payment apps to address vulnerabilities and enhance security features. Users are encouraged to keep their apps and operating systems up to date to benefit from these improvements.
Behavioral Analytics: Some systems employ behavioral analytics to detect unusual activity. By analyzing patterns in how a user typically interacts with their device and payment system, the technology can flag and prevent potentially fraudulent transactions.
Best Practices for Users

Use Strong Passwords: Avoid using easily guessable passwords. Instead, use a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters, and change your passwords regularly.
Enable Biometric Authentication: Whenever possible, enable biometric authentication for an added layer of security.
Monitor Transactions: Regularly check your account statements and transaction history for any unauthorized activity. Report any suspicious transactions to your bank immediately.
Be Wary of Public Wi-Fi: Avoid making payments over public Wi-Fi networks, which can be less secure and more susceptible to hacking. If necessary, use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet connection.
Install Security Software: Use security software to protect your device from malware and phishing attacks. Many mobile security apps offer features specifically designed to safeguard mobile payment information.
The Future of Mobile Payment Security

Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can enhance security by detecting and responding to threats in real-time. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies that human analysts might miss.
Quantum Cryptography: Quantum computing promises to revolutionize encryption methods, making it virtually impossible for hackers to crack encrypted data.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s decentralized nature and inherent security features could offer new ways to secure mobile payments and reduce fraud.

