Embracing the Future: How Telemedicine and Remote Health Monitoring are Transforming Healthcare

Remarkably, telemedicine and remote health monitoring (RPM) are changing the game in today’s quickly changing healthcare environment. Patients can now obtain high-quality care without leaving their homes because to these technological advancements in healthcare, which are also improving accessibility, efficiency, and personalisation. Let’s examine how these developments are influencing healthcare going forward.
The Rise of Telemedicine

Convenience and accessibility: By allowing patients to consult with medical professionals from the comfort of their homes, wait periods are decreased and travel requirements are removed. This is especially helpful for people who live in underserved or rural locations, where getting care could otherwise be extremely difficult.
- Advertisement -Cost Savings: By reducing needless ER visits and hospital stays, telemedicine can lower healthcare expenditures. For example, individuals and healthcare systems can save a lot of money by using virtual consultations and follow-ups in favour of in-person visits.
Improved Patient Engagement: Telemedicine facilitates communication between patients and healthcare professionals, which improves patient engagement and treatment plan adherence. Patients who regularly check in virtually are held more accountable and knowledgeable about their health.
The Power of Remote Health Monitoring
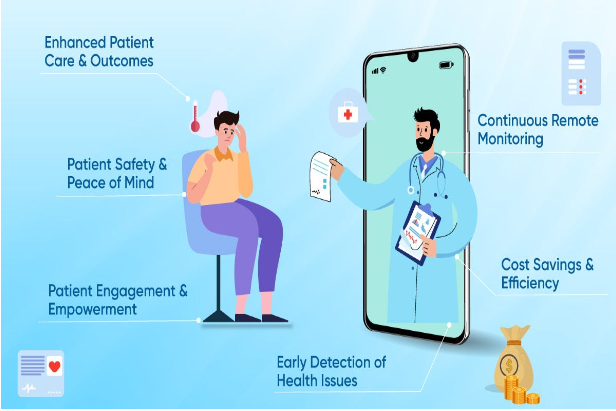
Real-Time Information and Prompt Intervention: RPM gadgets, including wearable sensors and home monitoring systems, are always gathering information on health indicators and vital signs. With the use of this real-time data, medical professionals can proactively identify any problems and take appropriate action to avoid difficulties and hospital admissions.
Improved Chronic Disease Management: RPM gives patients with long-term illnesses including diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease a method to closely monitor their health and modify their medications as necessary. This continuous monitoring lowers the risk of serious health events and aids in the better management of chronic conditions.
Patient Empowerment: RPM gives patients the ability to actively participate in their own health management. Patients can make educated decisions about their lifestyle and care by having quick access to their health data.
Technological Innovations Driving Change

Wearable Devices: Heart rate and sleep patterns are only a couple of the many health data that may be tracked by contemporary wearable technology, such fitness trackers and smartwatches. These increasingly advanced gadgets give precise and thorough health data that may be easily shared with medical professionals.
AI and Machine Learning:RPM and telemedicine are becoming more powerful thanks to machine learning techniques and artificial intelligence (AI). Large-scale health data can be analysed by these technologies to find trends, forecast results, and offer individualised treatment recommendations, all of which raise the standard of care.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs): A comprehensive and current picture of a patient’s health is provided to healthcare professionals by integrating telemedicine and RPM data with electronic health records (EHRs). Better diagnosis and customised treatment regimens are made possible by this all-encompassing strategy.
Challenges and Future Directions

Privacy and Security: It is crucial to protect the confidentiality and security of medical records. Since RPM and telemedicine depend on digital technologies, strong cybersecurity measures are necessary to guard patient data against security lapses and unauthorised access.
Reimbursement and Policy: RPM and telemedicine’s regulatory and payment environments are currently developing. To promote wider adoption and guarantee that providers are adequately reimbursed for remote care services, it is necessary to establish clear policies and equitable compensation methods.
Digital Divide: The digital divide may restrict access to RPM and telemedicine. It is imperative for equitable healthcare delivery that all patients, irrespective of their geographic location or socioeconomic position, have access to the required technology and internet connectivity.

